There’s a lot of bad advice floating around about “optimising for GEO.” Most of what you’ll read is just the same old SEO with a new label slapped on top, and while SEO is connected to GEO, treating them as the same thing is really misleading.
The reality is, you DO need SEO for GEO to work. SEO is the the foundation of GEO. But once that foundation is down, understand that GEO has its own logic, its own signals, and its own way of deciding whose content gets surfaced in AI answers. So repackaging SEO tactics and calling them GEO muddies the water.
That’s why we put this guide together. It’s everything we’ve learnt from running real experiments, seeing what works for our clients, and pressure-testing those same ideas on our own site.
Now, GEO is still early, and there isn’t really a checklist, the way there is with SEO. But there are practical steps you can take right now that will move the needle and put your SaaS in front of buyers – inside AI-driven search results.
(As this space shifts, we’ll keep coming back to refine this guide with what’s actually working on the ground.)
TL:DR
- SEO is still the foundation: LLMs can’t cite you if your site isn’t crawlable, structured, and credible. GEO builds on top of SEO, not instead of it.
- What GEO is: Making your SaaS visible in AI-driven search (Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini). Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) means AI now cross-checks live web data, so both on-site and off-site signals matter.
- Where GEO shows up in SaaS journeys:
- Early discovery: category definitions, industry-specific use cases, integration explainers.
- Mid-funnel: pricing tables, competitor comparisons, feature/security pages.
- Late stage: FAQs, onboarding docs, case studies, implementation guides.
- GEO fundamentals to bake in: entity clarity, topical depth, semantic coherence, structured data, Q&A-led sections, source credibility, freshness, cross-site corroboration, and AI-friendly content design.
- Our GEO optimization process:
- Phase 1: Strengthen SEO: solid technical SEO (crawl health, structured navigation, canonicalization), clean on-page optimization, genuinely useful content, strong UX signals, consistent measurement.
- Phase 2: GEO tactics: llms.txt file for guidance, keep critical info in plain HTML (not hidden in JavaScript), digital PR for contextual mentions and backlinks, aggressive cross-platform redistribution in native formats, citation-friendly Q&As, and freshness on priority pages.
- Measurement & governance: spot-check AI citations, track entity-driven queries, monitor reviews and off-site mentions, build content/schema QA workflows, run structured experiments, avoid keyword stuffing and generic FAQs.
What GEO Is (For SaaS) And Why It Matters Now
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) ensures your SaaS is visible in AI-powered searches. That could be Google’s AI Overviews, or ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, or Perplexity for the best solution in your category.
It rests on the same foundation SEO has always required: a well-structured site, authoritative content, and backlinks that signal credibility. That part hasn’t changed. What’s new about GEO is understanding how AI systems weigh those signals across the broader web, and then shaping your strategy so you actually show up in the answers they generate.
Why GEO Matters For SaaS
Now with more and more reports are coming out showing that people are finding Google less useful than AI-powered, and some proving that AI-chatbots are beating Google in referral traffic, GEO is becoming non-negotioable.
For example, a GrowthMemo study reveals that not only users are relying on AI for recommendations but are also seriously considering them. The traffic coming from LLMs like ChatGPT, Perplexity and Copilot sticks more to your site than what’s coming from Google.
That makes sense when you think about how AI search works: instead of handing them ten blue links to look into on their own, it distills the best information into one clear answer. It helps them move faster through that buying journey – hence bringing them closer to decisions quicker. So by the time a user clicks through, they’re past the casual browsing phase and they’re closer to a decision.
For SaaS, where buying decisions are complex and full of comparisons, that’s a huge advantage. If you become one of the brands that AI trusts enough to cite, you get in front of prospects right when they’re weighing options.
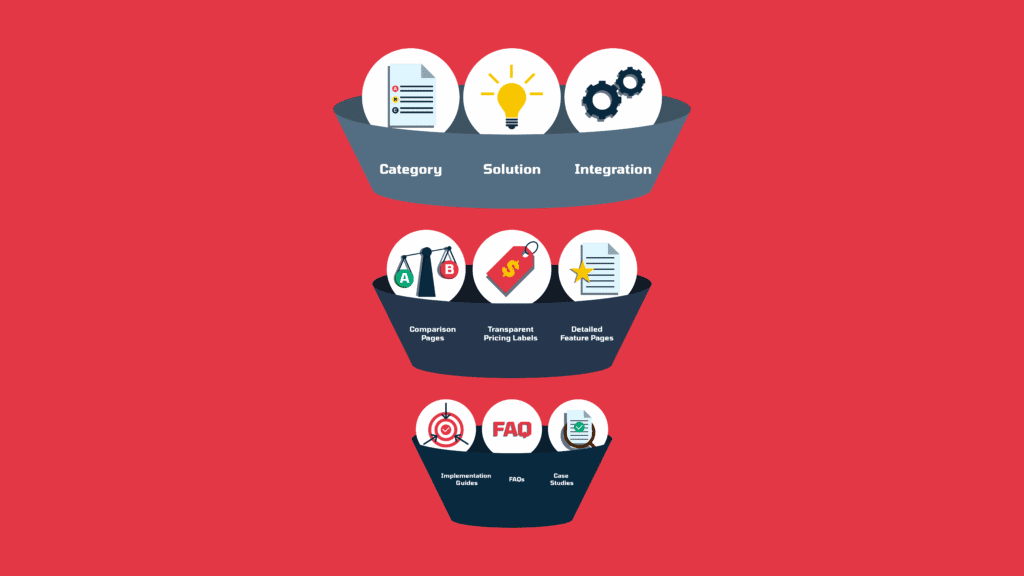
Where GEO Shows Up In SaaS Buyer Journeys
The impact of GEO shows up all along the SaaS buyer journey, from the moment someone first tries to understand a category, to when they’re weighing options, to the point where they’re ready to commit.
- At the early discovery stage, that means category pages, industry-specific solution pages, and integration-focused content – it’s all the kind of content AI can pull into an explanation when a user asks “what’s the best CRM for startups?” or “does this tool connect with Slack?”
- In the mid-funnel, prospects already know the category, and now they’re comparing. This is where your competitor comparison pages, transparent pricing tables, and detailed feature pages will work. These are the content types LLMs can lift directly into side-by-side breakdowns, surfacing your differentiators in the exact moment a buyer is weighing options. For example; “What features make Hubspot better than Salesforce for a bootstrapped SaaS?” or “Which of the top CRM tools provide better sales reporting?”
- And in the late stages, when the decision is close, GEO influences the confidence factors. Implementation guides, FAQs that address edge cases, and case studies often show up here. As do reviews and public sentiment around your brand and products. For example “What are common complaints about [your company]” or “What do reviews say about [your company]”
GEO Fundamentals To Bake Into Your SaaS Site
Before you get tactical with GEO, there’s a set of fundamentals you need to know about. These are baseline qualities AI systems look for when deciding whether to trust and cite your content.
- Entity clarity and consistency: Define your core entities (brand, product, features, integrations, industries, use cases) and use consistent naming, descriptions, and internal linking so LLMs can map you to the right category.
- Topical depth and coverage: Cover your category thoroughly, including all the features, use cases, integrations, industry angles – even if some topics have little or no search volume. Depth and relevance outweigh volume in GEO.
- Semantic coherence: Structure content so ideas flow logically. LLMs favor content that’s cohesive and purposeful rather than keyword-stuffed.
- Structured data essentials: Use schema types like Organization, Product/SoftwareApplication, FAQPage, HowTo, and Article. Fill in key properties such as pricing, version, operating system, and reviews, and always validate to ensure accuracy.
- Conversational, Q&A-led sections: Answer high-intent questions in short, factual blocks before expanding, and bring the bottom value up front. Add modular FAQs across product, pricing, security, and integration pages.
- Source credibility signals: Reference 4-6 authoritative, external sources where relevant. It shows research depth and boosts trustworthiness in AI parsing.
- Information freshness: Keep updating timestamps for pricing, feature pages, and integration docs so recency signals are clear to LLMs.
- Cross-site corroboration readiness: Make sure what you say on your site matches what’s said elsewhere (in reviews, articles, directories), so your story is consistent and verifiable.
- Content design for AI parsability: Use clear headings, short paragraphs, bullet lists, and comparison tables. Add descriptive filenames, transcripts, and alt text so engines can parse context from media too.
Our Approach to Optimizing SaaS Sites for GEO
Honestly, there is no definitive set of GEO tactics out there that guarantees visibility in LLM results, at least not yet.
And anyone who tells you otherwise is just dressing up SEO best practices and giving them a new name – which misses the point because SEO has its own importance.
ChatGPT and Perplexity are actively indexing Google and Bing, and you wouldn’t stand a chance in those engines without solid SEO. That’s the base – technical cleanliness, crawlability, and content that earns its place in the index. It’s what gets you seen in search and what these AI systems feed on to begin with.
GEO is then the step that comes after with strategies built around understanding of the filters, weights, and appraisal layers AI-powered search engines apply once they’ve pulled that indexed content in. That’s why we treat SEO and GEO as two separate but connected dimensions of visibility – one gets you into the system, the other gets you chosen inside the answer.
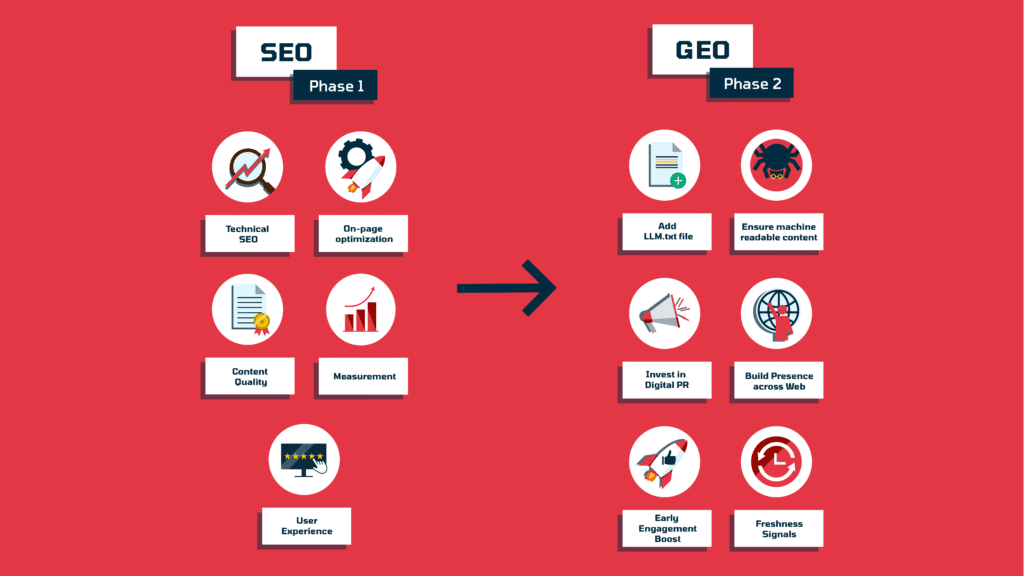
That’s why we separate our process into two phases.
Phase one is about doubling down on SEO basics and tightening them to a level where they actually support AI visibility.
Then phase two is GEO-specific: the experimental, LLM-specific tactics that sit on top of SEO and connect back to fundamentals like entity clarity, structured data, semantic coherence, topical depth, source credibility, freshness, and cross-site corroboration.
Here’s what the process looks like in practice:
Phase 1 – Strengthen SEO Fundamentals

Source: Growtika
- Technical SEO: Make sure your site is easy for search engines to crawl and index. That means clean URL structures, a regularly updated XML sitemap, proper canonical tags to avoid duplication, and careful handling of filter/parameter pages so they don’t create endless crawl loops. (Ps: This is just a quick overview of technical SEO is, but in practice it runs much deeper, from server configurations to log file analysis. But at minimum, getting these core elements right gives both search engines and AI systems a clean foundation to work with.)
- On-page optimization: Each page should have one clear purpose. Use headings to reflect that structure, align them with how people actually search, and write meta titles and descriptions that explain the value. For product, feature, and comparison pages, highlight the terms your audience already uses in demos, reviews, or support tickets. That makes your content more discoverable and also easier for AI systems to categorize.

Source: Hubspot
- Content quality: Create in-depth, genuinely useful content that solves specific problems, like feature explainers, integration guides, security overviews, or transparent pricing breakdowns. You want to build pages that someone would actually bookmark or share with their team.
- User experience: Navigation should feel intuitive, with clear paths from category pages down to features, integrations, and docs. Put yourself in the buyer’s place to make sense of what that should look like – a homepage that explains the category, feature pages that answer “how does it work?”, and blogs that show “how do I set it up?”. Engagement signals (like time on page or click-throughs between resources) follow naturally if the structure makes sense.
- Measurement: Keep track of how search engines crawl your site (crawl stats, index coverage reports), how your pages perform in organic search (impressions, clicks, CTR), and how users engage once they land (bounce rates, conversions).
Don’t Let GEO Miss You
Generative engines read differently than traditional search. If you want help structuring your site so AI notices your content, we’ve got you.
Phase 2 – Layer GEO-Specific Tactics
Add an llm.txt file
Just like you guide Google with robots.txt, guide LLM crawlers with an llms.txt file. Place it in your root directory and use it to point AI systems toward your most authoritative, structured content, such as canonical product pages, FAQs, pricing, integration guides, and category definitions.
Ensure your content is machine readablem
LLMs aren’t great with JavaScript-heavy rendering. So if something lives behind JS, like your pricing tables, your integration lists, your compliance details, those crawlers simply don’t see it. And if they can’t see it, they can’t include it in an output, no matter how important it is. That means even if a buyer is LITERALLY searching for you, your pricing, your product, your integrations, you could be invisible because the AI couldn’t retrieve the information. That’s why critical details need to live in clean, semantic HTML and not behind images, or under codes that AI crawlers can’t yet comprehend.
Invest in digital PR
Both Chatgpt and Perplexity have some preferred domains – some because they’ve struck million dollar deals with them and others because they’re very intentionally, manually whitelisted as trusted sources. Which means a mention on those sites gives you a straighter line into answers than ten smaller backlinks ever could. That’s where digital PR earns its keep. A well-executed campaign lands you coverage and places your product in the middle of conversations that LLMs already trust. And that has a double effect: you get the link-juice, but you also build contextual associations between your product and the problem it solves.
Traditional link building still matters, sure, but backlinks in isolation aren’t what these systems are looking for anymore. They’re cross-checking facts across the web, building patterns of “who solves what,” and that’s what makes contextual relevance.
Build a wider presence across web
Both ChatGPT and Perplexity evaluate content beyond your site. Their ranking configs weigh freshness, corroboration, click engagement, and coverage across multiple domains, not just whether your blog says something. So building a footprint matters. Every core piece of content should be redistributed into platform-native formats: LinkedIn posts, Reddit threads, Quora answers, Stack Overflow snippets, Discord discussions, and especially YouTube. Perplexity has been observed to weight exact keyword matches in YouTube videos, which means skipping video leaves visibility on the table. The wider and more consistent your presence, the more confidence an LLM has in citing you.
Give your content an early engagement boost
One of the ranking parameters surfaced for Perplexity is how much the first few hours of a page’s life matter. If your content gets early impressions, clicks, and solid dwell time, it sends a signal that what you published is worth pulling into answers. But when you leave it to sit, you risk being overlooked – which makes distribution no longer optional. You need to push your content where you know your audience is warm and attentive.
Depending on your product it could be Facebook, email newsletter, slack communities,or even a Reddit thread. Also use headlines that people actually want to click, and get those early eyeballs on the page. That initial velocity tells the model “this is worth it.”
Create citation-friendly page design
Add concise “answer blocks” on high-priority pages (home, product, pricing, integrations, docs). These short, direct explanations mimic how LLMs structure their outputs. Example: instead of burying your “What is [Product]?” definition halfway down the page, lead with it in a clear, scannable block that an AI can lift cleanly.
Give AI Freshness signals
AI models weigh recency more than traditional SEO. So keep updating timestamps, pricing tables, feature lists, and integration docs regularly, especially for fast-moving SaaS categories. Even small changes, like reflecting a new Slack or Notion integration the week it launches, send a freshness cue that makes your content more likely to surface in answers.
How to Measure GEO Impact for your SaaS Brand
One of the hardest things about GEO right now is that right now we don’t really have a proper analytics dashboard like we have for SEO. For the most part, you’d have to work with proxies – signals that tell you whether your content is being picked up, trusted, and repeated across AI systems.
And just as important, you need governance to keep quality from slipping as you scale.
Proxies for GEO Impact
- AI overview and assistant spot checks: The most direct proxy is running queries and logging whether your brand, product, or content gets cited in AI outputs. Tools like Peec.ai already automate this across Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and ChatGPT, with Ahrefs and SEMrush both building similar dashboards. These platforms let you track not just if you’re mentioned, but under what type of queries (branded, feature, integration, competitor) and how consistently.
- Branded and entity-related queries: Within Google search console track impressions and average position in traditional SERPs, AND in Google’s AI surfaces as they roll out. Then look at whether overall brand and entity mentions like your company name, product, or integrations are climbing. If both are trending up together, that’s a strong GEO signal and it tells you that your content is not only holding ground in search, it’s also being pulled into AI answers and nudging discovery across both layers.
- Assisted conversions and referral patterns: Google Analytics gives you the clearest read on whether you’re getting traffic from ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Copilot. If that referral traffic is growing, it’s a strong sign you’re surfacing in those systems. The next step is to look at how that traffic converts compared to traditional organic. Are AI referrals just driving visits, or are they bringing in higher-intent users who move further down the funnel? That split tells you whether your GEO work is simply generating visibility or actually earning you the kind of traffic that matters for revenue.
Content and Schema Quality Assurance (QA) Workflow
To give LLMs the best shot at citing you, every piece of content needs to clear a baseline QA before it goes live:
- Answer blocks: LLMs look for scannable, self-contained chunks of information to drop into their answers. Which is why every high-value page should include at least one clean, factual answer that could be pulled into an AI output, easily. If your explanation of “What is [product]?” or “How does [feature] work?” is buried halfway down the page, you’re making it harder for the model to use you.
- Schema validation: Schema is still unproven in terms of directly improving LLM comprehension, but it’s critical for SEO, and SEO is the base here. Google and Bing indexes are what ChatGPT and Perplexity pull from, so if schema helps traditional crawlers interpret your content cleanly, it indirectly helps GEO.
In SaaS, properties like pricing, integrations, version numbers, and reviews change constantly and schema is one of the key ways you surface those details to crawlers, which means if it’s outdated, you’re actively confusing the systems by giving them wrong/broken information to the index. That erodes trust fast. So keeping schema updated is one of the key ways to ensure the version of your product that Google, Bing, and by extension AI systems see is the same one buyers see on your site. - Entity linking: Internally link your brand, product, features, and integrations in a consistent way. This tightens context so that when an LLM parses your site, it can confidently map relationships (e.g. “[Product] integrates with Slack for sales reporting”). If you have messy or inconsistent entity mentions, you make it harder for AI systems to see you as a reliable reference in a given category.
- Source citations: Don’t just state claims, ground them in authoritative external references. LLMs weigh corroboration heavily. If you’re the only one saying something, or you don’t show your homework, you’re less likely to be cited. So include external links to trusted sources (prioritse the manually whitelisted sites) signaling that you’re not an isolated claim, but part of a broader consensus
- Recency signals: AI models weight freshness more aggressively than Google’s ranking algorithms ever did. Pricing tables, feature lists, integration docs, compliance details, all of these date fast in SaaS. So keep timestamping high-value pages and set a recurring update cadence.
Pitfalls to Avoid
- Keyword stuffing without entity clarity: You might rank in Google, but LLMs will skip you if they can’t connect the dots between your content and the category context.
- Thin or boilerplate FAQs: A weak Q&A section actively reduces trust. LLMs avoid citing vague or spammy answers.
- Ignoring corroboration: Even airtight on-site content won’t surface if it’s not reinforced off-site. You NEED industry articles, review sites, and community discussions echoing your positioning (hello Digital PR, and content repurposing), or LLMs won’t risk pulling you in.
- Stale information: Outdated docs, feature pages, or undated pricing are most potent killers for GEO. LLMs prioritize freshness because they don’t want to surface wrong answers.
Don’t Let GEO Miss You
Generative engines read differently than traditional search. If you want help structuring your site so AI notices your content, we’ve got you.
FAQs
How do I get my SaaS content cited in AI answers?
Citations come down to two things: machine-readability and cross-site corroboration.
On your site, critical information needs to live in plain HTML, not hidden behind JavaScript rendering. LLM crawlers aren’t great at executing JS, which means if your pricing tables, feature details, or compliance notes are locked behind scripts, they may never be read or retrieved. So keep those essentials in clean, structured blocks that AI can lift easily, like concise Q&As, transparent pricing tables, and feature definitions.
And secondly, AI systems cross-check what you say against the wider web. That means reviews, digital PR mentions, community discussions, and third-party articles all play a role in how you are perceived by LLMs. The more consistent and context-rich your story is across on-site and off-site touchpoints, the stronger your odds of being surfaced and cited.
Which schema types should SaaS teams implement first?
Start with the high-impact basics: Organization, Product (or SoftwareApplication), FAQPage, and HowTo. These give AI systems a clean way to understand who you are, what you offer, and how your product is used. Then add Article schema for blog and resource content.
How do we measure GEO success?
There isn’t one perfect KPI for GEO yet, but there are clear proxies you can track.
- AI citation tracking: Use tools like Peec.ai to monitor when and where your brand is cited inside ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google AI Overviews.
- Search Console trends: Track impressions and rankings for your brand, product, and integration queries in Google Search Console. Pay attention to both traditional SERPs and AI surfaces (AI overviews/AI mode) as they roll out. An increase across both is a strong GEO signal.
- Referral traffic and conversions (Google Analytics): Look at whether you’re getting direct referral traffic from ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Copilot. If it’s growing, AND converting at a higher rate than organic, that’s proof your visibility in AI search is paying off.
Final Thoughts
GEO is still early days, and its rules keep changing faster than any of us would like.
What we’ve shared here is the closest thing we’ve found to a working process: shore up SEO, add GEO-specific tactics on top of it, and keep a steady hand on measurement and upkeep.
It’s what’s working for us right now, and what’s working for our clients too (Check out this case study we’ve put together for some recent GEO wins we’ve had with a B2B SaaS).
We’ll keep refining this guide as the space evolves. But if there’s one takeaway, it’s this: the SaaS companies who get cited tomorrow are the ones laying the groundwork today.
If you’re not sure where you stand right now, that’s exactly what we have free discovery calls for. We’ll take a look at your SaaS site together and map out your quickest wins for LLM visibility.



