Broadly, there are two main ways you can enter ChatGPT’s brain – one is via the static memory of its training data, and the second is the live retrieval it runs when pulling an answer. The first part is, obviously, outside your control – meaning if your company didn’t exist before the cutoff, it won’t suddenly appear in ChatGPT’s baked-in memory.
Where you DO have control is in the live layer. From ChatGPT’s configuration settings (the reranker models, freshness scoring profiles) and retrieval parameters visible in the dev console, we are now sure that its system is constantly looking for recognizable entities, up-to-date information, and trusted sources to stitch into its replies. If you’re present across those signals, you’re far more likely to show up.
In this guide, we’ll translate those configuration-level insights into concrete strategies you can apply to your SaaS site.
TL:DR
- Clean up your entity hygiene. Standardize your brand name and descriptions across Crunchbase, LinkedIn, G2, Product Hunt, and your site’s schema with sameAs links.
- Keep content visibly fresh. Refresh cornerstone pages quarterly, add “last updated” dates, and keep sitemaps in sync.
- Write prompt-shaped answers. Use BLUF summaries, conversational flow, and extractable formats like tables, FAQs, and pros/cons.
- Build topic clusters. Cover your category broadly with hubs and spokes so you show up across multiple query variations (RRF rewards consistency).
- Earn third-party signals. Get mentioned by category anchors (the “HubSpot” of your niche) and collect authentic user reviews to build consensus.
- Publish decision-ready content. Ship real comparisons (YourTool vs Competitor) and integration guides with clear criteria, version dates, and HowTo schema.
- Make your site machine-checkable. Keep key info in plain HTML, validate schema, and avoid hiding content behind JS or PDFs.
- Control crawling. Keep robots.txt clean, consider llms.txt, monitor crawler logs, and ensure uptime and fast response times.
- Test and iterate. Run category-specific prompts monthly, track which sources get cited, and backfill gaps before competitors run away with them.
How ChatGPT’s Ranking Algorithm Works – A Quick Overview
To build an answer, ChatGPT moves through a series of steps that filter, score, and assemble content into something that feels balanced and trustworthy. Here’s how process looks like (a high-level overview):
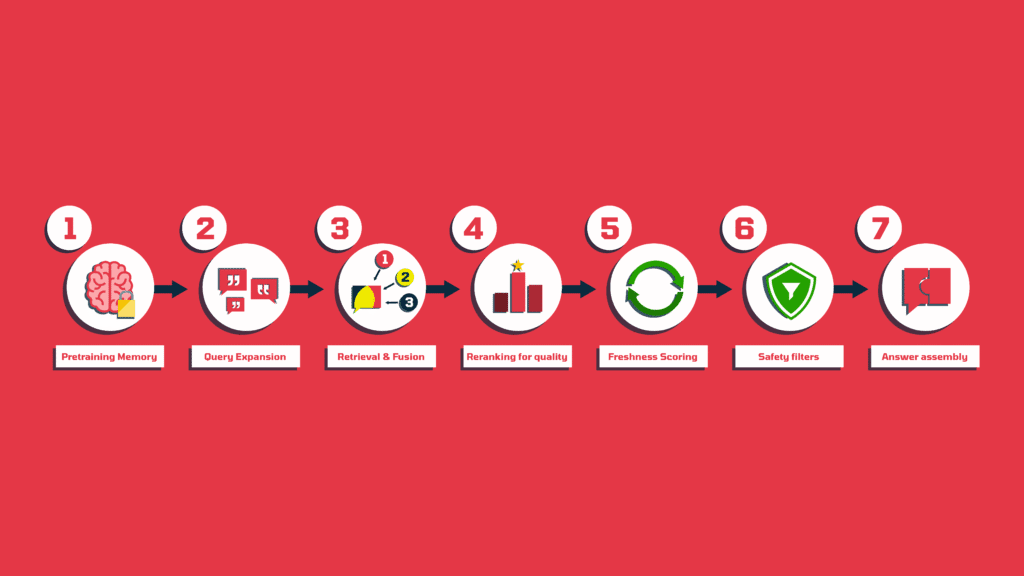
1. Pretraining memory
This part of ChatGPT’s brain that’s locked – you can’t make it into it, no matter how you strategize. It included information from places like Wikipedia, Crunchbase, G2 reviews, and major news sites. If your brand was visible in these places, when it was collecting initial training data, you start with a head start. If not, don’t worry, the real opportunity is in the live retrieval that powers today’s answers.
2. Query expansion (fan-out)
When a user asks something, ChatGPT doesn’t run just one search. It rewrites the query into variations to cover different phrasings and angles (called “query fan-out”). A prompt like “best CRM for startups under $70” can branch into “affordable CRM software” or “CRM with Slack integration under $70.” This is why topic clusters matter: they give the system multiple entry points to pull you in.
3. Retrieval and fusion
From that bundle of queries, ChatGPT pulls candidate pages from the web (and private connectors like Google Drive if a user has them enabled). Then it merges the results using Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) – a method that rewards sites appearing consistently across many variations. In other words, ranking #5 for ten related searches often beats ranking #1 for just one.
4. Reranking for quality
Next, a neural reranker (internally called ret-rr-skysight-v3) reshuffles the list. It favors pages that are structured, comprehensive, and easy to lift into an answer, things like tables, FAQs, step-by-steps, or clear comparison sections. Surface-level coverage might get retrieved, but depth and clarity keep you in the mix.

Source: Metehan.ai
This is a screenshot from ChatGPT’s internal configuration settings showing the active reranking model (ret-rr-skysight-v3). This parameter confirms that ChatGPT uses a neural reranker to reorder retrieved results based on relevance, quality, and authority before assembling its final answer.
5. Freshness scoring
ChatGPT has freshness filters always switched on. Pages with recent updates and visible “last updated” stamps are weighted more heavily than older, untouched guides. Even evergreen content needs polish to avoid looking stale next to a competitor’s refreshed version.
6. Safety filters
Pages cluttered with obfuscated code, hidden scripts, or suspicious markup can get flagged in this step. Even legitimate code samples need to be scoped cleanly; otherwise, the system may treat them as risky and drop them.
7. Answer assembly
Finally, ChatGPT stitches together the answer. For decision-level questions (e.g., “What’s the best CRM under $70?”) it tends to cite sources like review sites and comparison articles, then mention tools by name.
For more general prompts, it often just drops product names in passing. Either way, mentions shape perception, even when they’re not clickable.
Strategies to Get Mentioned in ChatGPT
The only practical way to getting mentioned in ChatGPT is to align your site with the exact filters and scoring layers the system uses. From entity hygiene to freshness and third-party proof, the strategies below are the ones that will gradually, but eventually get you there.
1. Strengthen Entity Hygiene
The easiest way to lose visibility in ChatGPT is to confuse it about who you are. If your brand shows up as “Flow CRM” on LinkedIn, “Flow Software” on Crunchbase, and “Flow Technologies” on G2, the system has no reliable anchor. And when the model isn’t sure which entity you are, it’s less likely to bring you into an answer at all.
So standardize your brand name, descriptions, and categories across every profile that matters, from LinkedIn to Crunchbase, G2, Product Hunt, and even Wikidata or Wikipedia if you qualify.
Parameters like enable_query_intent: true and vocabulary_search_enabled: true from the config show that the system is matching not just on keywords but on structured entities and terminology. So the clearer and more consistent you are, the less work ChatGPT has to do to figure out who you are.
The next level is schema. On your own site, implement Organization and Product/SoftwareApplication markup with sameAs links to those authoritative profiles.
That creates a graph that the model can connect together. When your Crunchbase, LinkedIn, and G2 all resolve back to your domain, the reranker sees you as a unified and trustworthy brand entity.
2. Keep Content Fresh (on a visible cadence)
Another signal based on the hints from ChatGPT’s own configuration; there’s a setting called use_freshness_scoring_profile: true, which basically means newer pages get extra weight. A brilliant guide from 2022 may still help people, but in the model’s eyes, it starts to look stale next to a competitor’s piece updated last quarter.
‘Freshness’ doesn’t mean you have to rewrite all your old stuff from zero; just make worthwhile, visible updates, and they’ll go a long way.
Here’s how to go about it in 3 phases:
Schedule the refresh
Decide in advance which pages you’ll revisit and when. Build a content refresh calendar and mark pages like comparisons, integrations, or data-driven posts as high priority.
Do the updates (make real content changes)
When your refresh date arrives, go beyond cosmetic tweaks and make some real content changes:
- Add new subsections for recent features, platform changes, or newly supported integrations
- Update context or examples to reflect current trends, tools, or pricing tiers
- Expand data: new metrics, fresh customer stats, updated benchmark tables
- Rework sections that are outdated or have new developments
- If something has changed fundamentally (architecture, limits, integrations), rewrite the relevant parts
Signal that an update occurred
After you’ve updated content, tell both humans and machines that you did it. A few ways to signal:
- Show a “Last updated: Month Year” stamp prominently
- Update <lastmod> in your XML sitemap so crawlers see a fresh timestamp
- Add a changelog note like “Added integrations with X and Y in July 2025”
- Maybe even a small “What’s new/Updated section” near the top
Be Seen by ChatGPT
Not sure how AI crawlers find content? We’ll guide you so your work actually gets on their radar.
3. Write Conversationally
ChatGPT thinks in prompts because users don’t type “CRM software startup cheap” into the model. They’ll say something like “I run a six-person sales team, I need a CRM under $50 that integrates with Slack.” If your content doesn’t feel like it could slot into that kind of answer, it’s harder for the system to lift you in.
The fix is to write in a way that mirrors how people actually ask for help.
-> Start pages with a clear, 2-3 sentence answer right at the top (the BLUF format). That’s the snippet a model can grab cleanly.

-> Then expand with context on the trade-offs, the setup steps, and the use cases. Keep the flow conversational but structured.
How you present your content matters too.
Extractable sections like tables, bullet lists, FAQs, and pros/cons are easier for the reranker to work with than long, unbroken walls of text (human readers don’t like that either). Overall, just make your pages sound like natural, human answers to the kinds of questions your buyers would actually ask out loud. The more your content feels “answer-shaped,” the higher the chance ChatGPT can weave it into its own replies.
4. Build Topic Clusters that Win Fusion (RRF advantage)
One query rarely decides whether your brand gets mentioned because ChatGPT runs a whole family of related searches behind the scenes, then fuses them together using Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF), evident from the (rrf_alpha: 1) parameter.

Source: Metehan.ai
As we discussed earlier, the math behind it rewards consistency, meaning that a site that shows up in the top 5 across ten different searches scores much higher than a site that lands #1 for just one.
This is why clusters are vital for getting mentioned in ChatGPT.
A hub page that covers the big picture, supported by sub-pages that dig into role-specific needs, budget tiers, integrations, and industry angles, gives you many more chances to show up in the system’s fan-out queries. When ChatGPT merges those results, your brand has multiple touchpoints feeding into the final list.
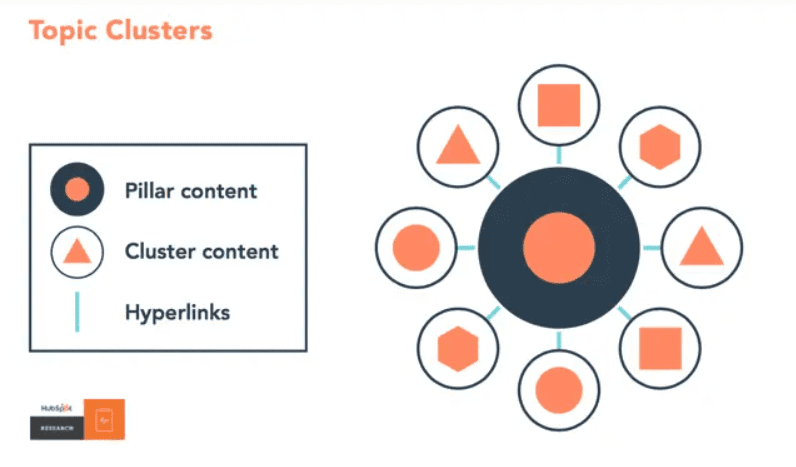
Source: Hubspot Blog
So this way you’re not betting on one doorway; you build a neighborhood of content where every page reinforces the others. That makes Reranker see you as authoritative across the whole space, not just 0.001% of it.
5. Leverage Trusted Data Sources
Before ChatGPT writes you into an answer, it looks for consensus across trusted sources. That’s why you’ll often see review sites, comparison roundups, and third-party explainers sitting at the core of its citations when a user is close to making a decision.
There are two layers to build here:
- Category anchors. Every industry has its “HubSpot” or “Semrush”, the big names whose content and lists get recycled everywhere. So when you get mentioned or linked by these players, whether in a roundup, a comparison, or even a contextual mention inside a blog post, it’s like an endorsement that the model takes seriously. The same goes for high-authority outlets like TechCrunch or trusted analyst blogs in your niche.
- User validation. The other side of the consensus is social proof. Reviews on G2 and Capterra, testimonials marked up with Review schema, and even posts from real customers on LinkedIn or X all feed into the footprint ChatGPT sees.
Ideally, you should combine both. It helps you anchor yourself in the big-name sources that define your category, and keep a steady flow of reviews and stories from actual users. That way, ChatGPT sees your name coming from authoritative voices and customer voices at the same time, it has every reason to treat you as a safe inclusion in the answer.
6. Make Your Site Machine-Readable
ChatGPT relies on a mix of keyword lookups and semantic embeddings, but those only work if the core information is accessible in a clean format.
That means your pricing, feature lists , and integration details need to live in plain HTML, not hidden inside JavaScript widgets or buried in PDFs.
Schema types like FAQPage, HowTo, Review, and Article make it easier for ChatGPT to understand what each section of your site is about. The config shows pages that are easy to parse and properly labeled get a head start in the retrieval pool.
So build your site for machines as much as for people. If an LLLM crawler can scan your page and extract the key points without heavy lifting, you’ve already cleared one of the earliest hurdles in the process.
7. Build Decision-Ready Content
When users turn to ChatGPT for buying advice, they often prompt the LLM in 2 ways: “Which tool is best for me?” or “Will this tool work with what I already use?” The system treats both as decision-level intent, and the config backs this up with enable_query_intent: true. To match those queries, you need two types of pages:
- Comparisons and best-for lists. Create dedicated [YourTool] vs [Competitor] pages and Best [Category] for [Use Case] roundups. Make sure to have consistent sectioning which clearly explains the use case fit, integrations, learning curve, pricing, and support. Add version dates and citations so your claims are easy to verify and stay fresh.
- Integration and compatibility guides. Publish standalone pages for each major integration (Slack, Notion, Salesforce, HubSpot). Show real setup steps, troubleshooting notes, and scope limits. Add HowTo schema so the machine sees the structure, and keep screenshots up to date.
These are the pages ChatGPT is most likely to pay attention to when answering decision-level queries because they look like safe, comprehensive resources to rely on.
These pages cover the exact long-tailed prompts that retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems fan out into during tool selection, giving the system many chances to include you via these guides.
8. Control Crawling and Indexing for LLMs
If crawlers get blocked, time out, or hit dead ends, your content never makes it into the retrieval pool in the first place. That’s why crawl hygiene matters just as much for AI visibility as it does for Google SEO.
->So keep your robots.txt clean and logical.
->Don’t accidentally block pages that carry core information like pricing, docs, or onboarding flows.
-> Consider adding an llms.txt file too, it’s still early days, but it signals permissions and preferences to AI crawlers the same way robots.txt does for search engines.
On the technical side, watch server performance. Slow time-to-first-byte (TTFB) or flaky uptime can cause crawlers to abandon requests, leaving gaps in what gets indexed.
9. Measure, Prompt-Test, Iterate
ChatGPT’s retrieval and reranking layers keep shifting with time, so you need a repeatable way to see how your brand is surfacing. The simplest way to do that today is with tools built for AI visibility like Peec.ai – it can run your category prompts inside ChatGPT on a schedule and log when your brand appears, what sources were cited, and how often competitors are mentioned.
Here’s how to go about it:
- Define your prompt set. Build 15–20 prompts that mirror real buyer questions (e.g., best [tool] for a 10-person startup under $50, integrates with Slack).
- Automate the runs. Use Peec.ai to test these prompts monthly and record whether your brand shows up.
- Track the sources. Note which domains ChatGPT is pulling from – review sites, comparison blogs, your docs, or competitors’ PR hits.
- Watch competitor share. Run the same prompts for 3–5 key rivals to see if their mentions are trending faster than yours.
- Align with your own data. Compare AI mentions against impressions for branded + category queries in Search Console. When both are rising together, it’s a strong signal that your optimization is working.
Final Thoughts
The way ChatGPT decides which brands to mention is now much less of a mystery. From the configurations we now know about most of the levers (reranker models, freshness scoring, and intent detection) and thankfully, most of them are within our reach. The question is how to put that knowledge into practice.
Here’s a simple sequence to get started:
- Audit your footprint. Check if your brand identity is consistent across Crunchbase, LinkedIn, G2, Product Hunt, and your own schema. Clean up discrepancies.
- Pick your cornerstone pages. Choose the 5–10 assets that matter most (comparisons, integrations, reviews, pricing) and schedule quarterly refreshes with visible “last updated” stamps.
- Map your third-party gaps. Identify which review sites, roundups, and category anchors mention your competitors but not you. Build a plan to close those gaps with PR or partnerships.
- Build your prompt set. Create 10–15 prompts a buyer would actually ask, run them monthly, and track what sources are surfacing. Adjust your content footprint based on what you find.
If you keep doing this steadily, in a few months, you’ll have a presence so solid built on the web that ChatGPT wouldn’t be able to ignore.
Want us to shortcut the process? Book a call, and we’ll map out exactly how your SaaS can become “mention-worthy” in ChatGPT, from entity cleanup to decision-ready content.
Be Seen by ChatGPT
Not sure how AI crawlers find content? We’ll guide you so your work actually gets on their radar.
FAQs
Can I buy mentions in ChatGPT?
No. There’s no paid slot or sponsorship model that guarantees your brand shows up in ChatGPT’s answers. Mentions are a byproduct of how the system retrieves and validates information. The only way in is to make your content recognizable, consistent, and reinforced by third-party proof so the model feels confident including you.
Do nofollow links matter to ChatGPT?
Yes. Even if a link is nofollowed, the mention itself still helps shape the context around your brand because ChatGPT doesn’t rank sites the way Google does, it looks for consensus. So a mention in a reputable source, whether it carries a followed link or not, still contributes to the confidence the system has in using your name.
How long does it take to start getting mentioned in ChatGPT?
Expect weeks to months, not days. It’s a compounding process: the more consistent your presence across sources, the more signals accumulate for ChatGPT to trust you. It’s like building authority in layers – entity hygiene, fresh content, third-party mentions, and reviews. Once all those layers stack up, mentions begin to appear more regularly.