TLDR
- Managing LLM crawlers requires a comprehensive bot policy for llms to protect valuable content from unauthorized access.
- Managing LLM crawlers requires a comprehensive bot policy for llms to protect valuable content from unauthorized access.
- Implement a multi-level framework that includes governance, technical enforcement, legal measures, and optimization.
- Establish clear access rules for each crawler by using Robots.txt, HTTP headers, and monitoring tools.
- Regularly review and refine your policies based on monitoring results and evolving bot behaviors.
- Maximize AI-driven visibility while safeguarding your SaaS resources and proprietary information
LLM crawlers have become a common presence on SaaS websites. While some of these crawlers are benign, even beneficially driving visibility through AI-generated answers, others can be detrimental to your business. Resource-hungry bots can strain your website’s performance, but even more concerning are those appropriating proprietary information to fuel competitor models.

For SaaS companies, this situation carries high stakes:
- Protecting IP and performance: Documentation, integration guides, and pricing pages are valuable assets that must be safeguarded from unauthorized access.
- Maximizing AI-driven visibility: When allowed bots index your content correctly, your product can appear in high-value AI answers that drive conversions and grow your business.
Here we offer a practical playbook to address these concerns. We outline a multi-level framework combining governance, technical enforcement, legal reinforcement, and optimization. Designed for implementation in under 90 days, this approach is both effective and defensible to regulators, auditors, and internal stakeholders alike.
Multi-Level Framework Overview
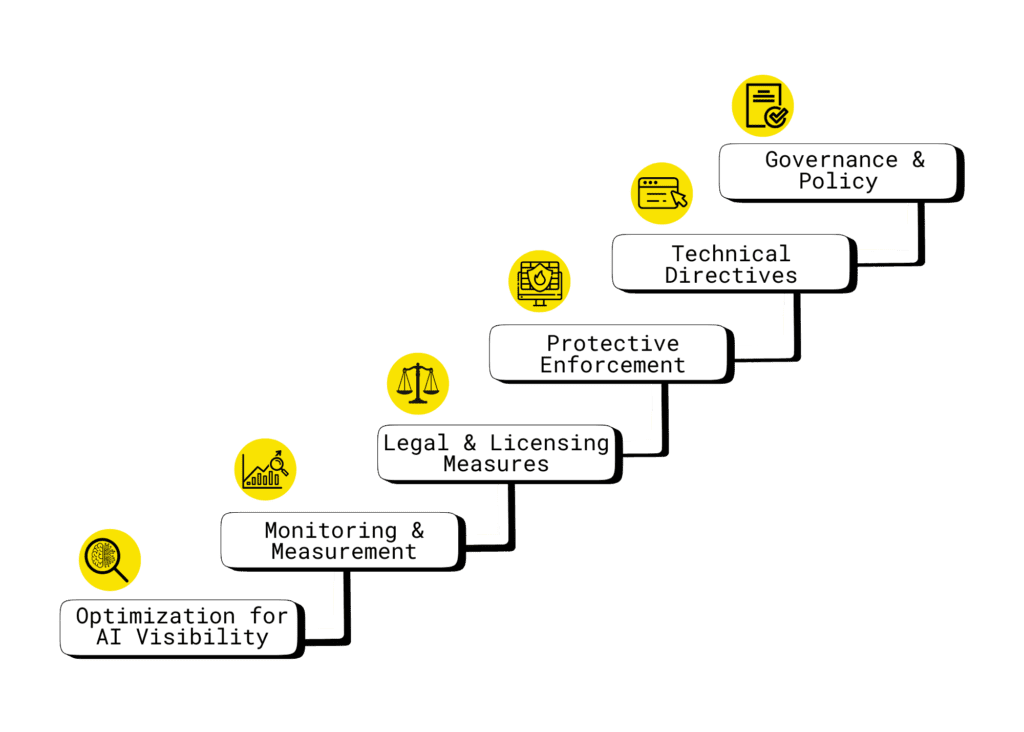
Layer 1: Governance & Policy
Before implementing any technical controls, you need to set the foundation for how your organization manages LLM crawlers. This is where you take control and make deliberate decisions about which crawlers can access your content, under what conditions, and why. You can access a downloadable AI bot governance policy template here.
- Inventory all crawlers: This document should catalog each LLM crawler you’ve identified (GPTBot, PerplexityBot, Google-Extended, etc.).
- Categorize by purpose: Identify whether it is content training, information retrieval, or autonomous actions.
- Decide allow/limit/block: Clearly record your strategic decision along with your reasoning, keeping it aligned with business goals and compliance obligations.
- Maintain governance docs: One authoritative record to justify choices against business or compliance challenges.
Layer 2: Technical Directives
Once your governance policies are defined, it’s time to put them into action. These are the mechanisms that enforce your decisions and guide crawlers on what they can and cannot access:
- Robots.txt: Define path-level restrictions for specific user-agents, including standard disallows and advanced dynamic serving (e.g., different responses by user agent). Serves as the core access control mechanism. Learn more in Google’s official guide to robots.txt.
- Page-level directives: Use <meta name=”robots”> and X-Robots-Tag headers to control indexing of sensitive pages.
- Licensing JSON-LD/XML: Provide usage policies in machine-readable formats.
- Restricted sitemaps and llms.txt: Provide AI crawlers with explicit signals about allowed vs. restricted content. For a deeper dive into what llms.txt is, see our article.
Layer 3: Protective Enforcement
Even with technical directives in place, some crawlers may attempt to bypass your rules. Protective enforcement ensures your site actively defends against unauthorized or risky bots:
- Server-side blocking: Use NGINX, Apache, or similar servers to block or rate-limit unverified or unwanted bots.
- rDNS/IP checks: Only allow bots whose IP addresses resolve to expected domains, preventing IP spoofing. For a detailed explanation of reverse DNS and its security applications, see Cloudflare’s guide on reverse DNS.
- Rate limiting & throttling: Monitor traffic for suspicious spikes and respond with 429 Too Many Requests to slow or stop excessive crawling. Learn more about how these mechanisms work in this guide on API rate limiting and throttling.
- HTTP status codes:
- 403 – Forbidden: Deny access to unauthorized bots.
- 451 – Unavailable for legal reasons: Block content that cannot be served due to legal restrictions.
- 452 – Proposed code for “LLM access denied”: Use a custom status code to explicitly indicate that AI crawlers are not permitted to access the resource.
- 403 – Forbidden: Deny access to unauthorized bots.
Managing AI crawlers responsibly
AI crawlers are showing up more and more, and most teams aren’t sure what they should allow. We help you sort through it and set rules that actually protect your site.
Layer 4: Legal & Licensing Measures
Some protections require more than technical enforcement, legal and licensing measures ensure your rights and policies are clear and actionable:
- Terms of Service updates: Explicitly prohibit unauthorized AI training or use of your content.
- Footer notices: Ensure all crawlers consistently encounter licensing and usage information on every page.
- Watermark sensitive content: Combine technical and legal measures to reinforce content ownership and usage restrictions.
- Machine-readable licensing: Provide JSON-LD or XML license files and reference them in robots.txt to communicate usage policies to automated systems.
Layer 5: Monitoring & Measurement
Before you can optimize or refine your LLM crawler strategy, you need to see what’s actually happening on your site. This layer helps you track, verify, and measure bot activity so your decisions are based on real data:
- Enable log analysis: Collect and review logs at both CDN and origin levels (e.g., Cloudflare, AWS CloudWatch) to monitor crawler activity.
- Track high-value pages: Focus on documentation, pricing, changelogs, and onboarding flows to see which content is accessed most.
- Detect spoofing: Identify headless browser signatures, bursty traffic patterns, and unusual referrers to catch potential impersonation.
- Set alerts: Configure automated notifications for blocked requests, suspicious activity, or abnormal crawl patterns.
- Tie to KPIs: Evaluate whether LLM visibility improves demo signups, trials, or support deflection.
Layer 6: Optimization for AI Visibility
Once you’ve secured and monitored your site, it’s time to optimize your content so AI crawlers can understand and prioritize it effectively. This layer ensures the right pages get surfaced in AI-generated answers, driving visibility and engagement:
- Technical clarity: Use clean HTML, structured headings, descriptive alt text, and canonical URLs to make content easy for AI crawlers to understand.
- Sitemaps with freshness signals: Keep lastmod dates accurate and up to date to highlight recently updated content.
- llms.txt adoption: Explicitly highlight which content should be prioritized.
- Hub pages: Create canonical, authoritative resources that are most likely to be cited by AI systems.
Execution Playbook (90-Day Plan)
To turn the multi-level LLM crawler framework into actionable results, this 90-day playbook provides a step-by-step roadmap. Each phase focuses on specific objectives, from auditing and governance to technical safeguards, optimization, monitoring, and refinement, ensuring your SaaS site is protected while maximizing AI visibility. The table below shows how each phase of the playbook maps to the strategic framework layers:
| 90-Day Plan | Corresponding Framework Layer(s) | Key Focus / Actions |
| Weeks 1–2: Inventory & Governance | Layer 1: Governance & Policy | – Audit logs to identify LLM crawlers: Review server, CDN, and analytics logs to identify which AI bots are accessing your site.- Document allow/limit/block decisions: Record each decision along with your reasoning, ensuring alignment with business goals and compliance requirements. |
| Weeks 3–4: Technical Safeguards | Layer 2: Technical Directives & Layer 3: Protective Enforcement | – Update robots.txt and meta tags: Configure path-level restrictions and page-level directives to control crawler access.- Implement rate limiting, throttling, rDNS/IP: Protect servers from excessive requests and ensure only legitimate bots gain access. |
| Weeks 5–8: Optimization & Monitoring | Layer 5: Monitoring & Measurement & Layer 6: Optimization for AI Visibility | – Enhance structured data, sitemaps, and hub pages: Improve technical clarity and highlight authoritative content for AI visibility.- Set up log-based monitoring, spoofing detection: Track crawler activity, identify suspicious patterns, and ensure bots comply with access rules. |
| Weeks 9–12: Review & Refine | Layer 1, 5 & 6 (Governance, Monitoring, Optimization) | – Measure impact on trials, signups, and traffic: Evaluate how AI visibility and crawler management affect key business metrics.- Adjust allow/block lists accordingly: Refine crawler access based on insights and observed behavior.- Share insights with Product, Legal, and Sales teams: Ensure cross-functional alignment and incorporate feedback into future strategy. |
Practical Snippets & Examples
To make implementation easier, here are concrete examples of configurations and code snippets you can use to manage LLM crawlers, enforce access policies, and signal licensing restrictions.
- Robots.txt for blocking specific crawlers:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Disallow: /
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Disallow: /private/
User-agent: Google-Extended
Disallow: /
- NGINX server-level blocking for specific crawlers:
if ($http_user_agent ~* (GPTBot|ChatGPT-User|OAI-SearchBot)) { return 403; } - rDNS verification for allowed crawlers (pseudocode):
if (ua in allowlist) {
rdns = reverse_dns(client_ip)
if (ua == "GPTBot" && rdns endsWith("openai.com") && forward_dns(rdns) == client_ip) { allow }
else { rate_limit_or_block }
}
- Meta tags and HTTP headers for crawler control and licensing:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, noarchive, noai"> X-Robots-Tag: noindex, noarchive X-Legal-Notice: Unauthorized use of this content for AI training is prohibited. X-License-Info: https://example.com/ai-license.json - Restricted sitemap example to signal disallowed pages to crawlers:
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/restricted-page</loc>
<lastmod>2024-07-24</lastmod>
<changefreq>never</changefreq>
<priority>0.0</priority>
</url>
</urlset>
Tools & Platforms
To effectively manage LLM crawlers and protect your site, having the right tools and platforms is essential. These solutions make it easier to enforce policies, monitor activity, and respond to anomalies in real time, so you can safeguard sensitive content while maximizing AI-driven visibility. Here is a election of tools that help SaaS teams implement layered controls efficiently:
Bot Management: Cloudflare Bot Management, AWS Bot Control, Fastly
- Identify and block unwanted bots at the network or CDN level.
- Set rules for known LLM crawlers and customize behavior for suspicious traffic.
- Protect server resources while ensuring legitimate bots can access allowed content.
Monitoring & Logging: AWS CloudWatch, Splunk, for CDN log analysis
- Collect detailed logs of crawler activity across servers and CDNs.
- Detect anomalies such as bursty traffic, spoofed user-agents, or unexpected IP ranges.
- Set automated alerts to respond quickly to suspicious or unauthorized access.
CMS Integrations & Dynamic Controls: WordPress plugins, Cloudflare Workers for dynamic robots.txt
- Implement page-level rules directly within your CMS without manual edits.
- Dynamically serve different robots.txt or meta tag rules depending on the crawler or user-agent.
- Combine with other enforcement layers for more granular, real-time control.
Bottom Line
Managing LLM crawlers is about controlling who accesses your content, how they interact with it, and why. Effectively managing these crawlers balances protection and opportunity:
- Protect proprietary assets: Safeguard documentation, pricing, and research from unauthorized access.
- Maximize AI-driven visibility: Ensure allowed crawlers index your content correctly to appear in high-value AI answers.
- Defend your choices legally and technically: Layer governance, technical controls, enforcement, licensing, monitoring, and optimization for a defensible, auditable approach.
This is a moving target. Crawler behaviors evolve, new bots appear, and AI platforms update their practices. So, revisit your policies quarterly, refine your allow/block lists, and adjust your technical controls to stay ahead.
Next steps: Implement the multi-level framework outlined in this guide, track results through your monitoring tools, and optimize your content for AI visibility. For expert support, Singularity Digital can help SaaS teams build a tailored LLM crawler strategy, from policy design to enforcement and optimization.For a deeper dive into LLM crawlers and founder-friendly strategies, check out What Are LLM Crawlers (How Founders Should Respond).
Managing AI crawlers responsibly
AI crawlers are showing up more and more, and most teams aren’t sure what they should allow. We help you sort through it and set rules that actually protect your site.



